https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/7276
- Also known as
- CTS (carpal tunnel syndrome);
ATTR; (transthyretin derived amyloid)
CTS1;
PALB; prealbumin
TBPA;Thyrocin binding prealbumin
HEL111; human epididymis luminal protein
111HsT2651 - Summary
- This gene encodes one of the three prealbumins, which include alpha-1-antitrypsin, transthyretin and orosomucoid. The encoded protein, transthyretin, is a homo-tetrameric carrier protein, which transports thyroid hormones in the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid. It is also involved in the transport of retinol (vitamin A) in the plasma by associating with retinol-binding protein. The protein may also be involved in other intracellular processes including proteolysis, nerve regeneration, autophagy and glucose homeostasis.
- Mutations in this gene are associated with amyloid deposition, predominantly affecting peripheral nerves or the heart, while a small percentage of the gene mutations are non-amyloidogenic.
- The mutations are implicated in the etiology of several diseases, including amyloidotic polyneuropathy, euthyroid hyperthyroxinaemia, amyloidotic vitreous opacities, cardiomyopathy, oculoleptomeningeal amyloidosis, meningocerebrovascular amyloidosis and carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) . [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017]
- Expression
- Restricted expression toward liver (RPKM 2070.5) See more
- Orthologs mouse all
- Preferred Names
- transthyretin
- Names
- epididymis luminal protein 111
- prealbumin, amyloidosis type I
- thyroxine-binding prealbumin
- Conserved Domains (1) summary
-
- smart00095
Location:27 → 147 - TR_THY; Transthyretin
- smart00095
Related articles in PubMed
- Unusual duplication mutation in a surface loop of human transthyretin leads to an aggressive drug-resistant amyloid disease. Klimtchuk ES, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2018 Jul 10. PMID 29941560,
- Kinetic analysis of the multistep aggregation pathway of human transthyretin. Sun X, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2018 Jul 3. PMID 29915031,
- Characterization of Non-amyloidogenic G101S Transthyretin. Wakita Y, et al. Biol Pharm Bull, 2018. PMID 29607936
- Exploring the Influence of Mutation on Transthyretin Aggregation in Heart Disease. Sharma A, et al. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des, 2018. PMID 29564986
- [Transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy - three Hungarian cases with rare mutations (His88Arg and Phe33Leu)]. Csillik A, et al. Ideggyogy Sz, 2016 Jul 30. PMID 29465889
GeneRIFs: Gene References Into FunctionsWhat's a GeneRIF?
- serum prealbumin, and its changes were independent predictors of worse prognosis in acute kidney injury (AKI), and could be potential surrogates to better predict 90-day mortality.
- T139R mutation may expose the buried regions of TTR protein which help in the self association and the increase in the stability may help in the TTR deposition. Structural analysis indicated that F and H strands of TTR are more prone to aggregation. Thus, T139R mutation might cause these residues to be aggregation prone and change in folding rate and validated TTR monomer in diseased cases by Western blot analysis.
- High TTR expression is associated with hypertriglyceridemia.
- Our study characterizes G101S TTR as a stable and N-glycosylable TTR, which may be linked to its non-amyloidogenic characteristic. G101S TTR had slower rate of tetramer dissociation and lower propensity for amyloid fibril formation, especially at mild low pH (4.2 and 4.5), and was likely to have strong hydrophobic interaction among TTR monomers, suggesting relatively higher stability of G101S TTR compared with WT TTR.
- studies of a unique duplication mutation explain its diflunisal-resistant nature, identify misfolding pathways for amyloidogenic TTR variants, and provide therapeutic targets to inhibit amyloid fibril formation by variant TTR.
- At physiological temperature, the monomeric intermediate formed by wild-type TTR under mildly acidic conditions rapidly aggregates into species that are invisible to NMR, leading to loss of the NMR signal at the same rate as the turbidity increase.
- We report here three non-related Hungarian cases of transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy with non-Val30Met mutations (His88Arg in two cases, Phe33Leu in one case) Early diagnosis is essential as the early introduction of causal therapy (tafamidis) slows progression and prolongs survival
- A novel amyloidogenic TTR mutation was found in a Dutch family
- Patients with ATTRV30M amyloidosis in non-endemic areas and patients with non-V30M ATTR amyloidosis occurred more frequently than previously believed, and their clinical manifestations were diverse. Hereditary transthyretin (ATTR) amyloidosis is a life-threatening, autosomal dominant, systemic amyloidosis caused by mutant transthyretin. In addition to ATTRV30M in endemic and non-endemic areas, more than 140 non-V30M mutations occur worldwide. (Jan 2018)
- Results indicate that TTR stability is important for its recently described functions in assisting Abeta transport at the BBB and at the liver and also in regulating LRP1 levels and activity. TTR stabilization can serve as an avenue to increase both Abeta elimination and LRP1 levels, which in turn will further participate in Abeta clearance. ..
- Moreover, HepG2 cells incubated with Aβ in the presence of WT TTR,
but not L55P TTR, showed an increased number of lysosomes. Further, in
the presence of WT TTR, Aβ peptide colocalized with lysosomes,
indicating that only stable TTR assists Aβ internalization, leading to
its degradation. Finally, we demonstrated that only stable TTR can
increase LRP1 levels.: TTR stabilization
exerts a positive effect on Aβ clearance and LRP1 levels, suggesting
that TTR protective role in AD is dependent on its stability. These
results provide relevant information for the design of TTR-based
therapeutic strategies for AD.
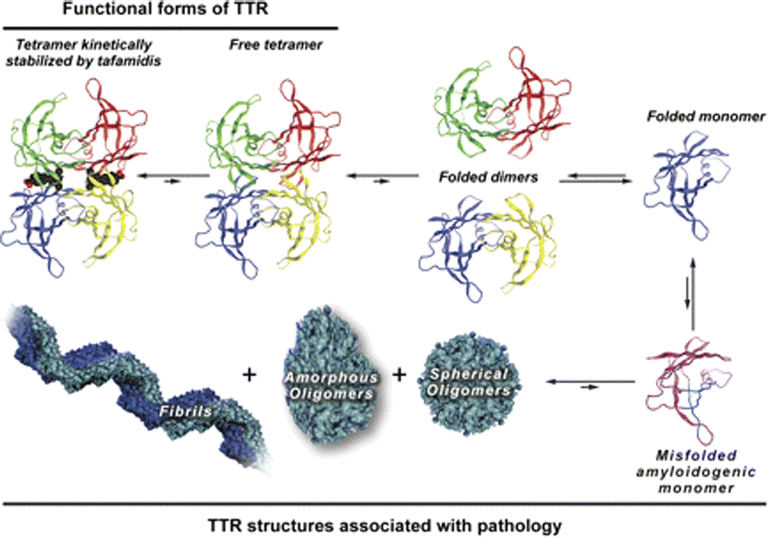
Transthyretin Structure
Peptide sequence Precursor https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_000362.1
Different mutations: Early dg important.
v30m, amyloidogenic mutation of TTR,
V30M mutations (Swedish)
nonV30M mutations
F33L (Hungarian)
H88R (Hungarian)
A65G (Dutch)
G121S,(Japanese) more stabile TTR , non amyloidogenic mutation
Peptide sequence Precursor https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_000362.1
##Evidence-Data-END## FEATURES Location/Qualifiers source 1..147 /organism="Homo sapiens" /db_xref="taxon:9606" /chromosome="18" /map="18q12.1" Protein 1..147 /product="transthyretin precursor" /note="prealbumin, amyloidosis type I; thyroxine-binding prealbumin; epididymis luminal protein 111" /calculated_mol_wt=13761 sig_peptide 1..20 /inference="COORDINATES: ab initio prediction:SignalP:4.0" /calculated_mol_wt=2144 mat_peptide 21..147 /product="transthyretin" /calculated_mol_wt=13761 Region 27..147 /region_name="TR_THY" /note="Transthyretin; smart00095" /db_xref="CDD:128406" Site 72 /site_type="other" /experiment="experimental evidence, no additional details recorded" /note="Phosphoserine. {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P02767}; propagated from UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot (P02766.1)" Region 135..139 /region_name="Thyroid hormone binding" /experiment="experimental evidence, no additional details recorded" /note="propagated from UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot (P02766.1)" CDS 1..147 /gene="TTR" /gene_synonym="ATTR; CTS; CTS1; HEL111; HsT2651; PALB; TBPA" /coded_by="NM_000371.3:137..580" /db_xref="CCDS:CCDS11899.1" /db_xref="GeneID:7276" /db_xref="HGNC:HGNC:12405" /db_xref="MIM:176300" ORIGIN 1 mashrllllc laglvfvsea gptgtgeskc plmvkvldav rgspainvaV hvfrkaaddt 61 wepfasgkts esgelhgltt eeefvegiyk veidtksywk algispfheh aevvftands 121 gprrytiaal lspysystta vvtnpke //Preproproetein 147- signal protein 20 = TTR 127 a.a.
Different mutations: Early dg important.
v30m, amyloidogenic mutation of TTR,
V30M mutations (Swedish)
nonV30M mutations
F33L (Hungarian)
H88R (Hungarian)
A65G (Dutch)
G121S,(Japanese) more stabile TTR , non amyloidogenic mutation